(Maria Tirado)
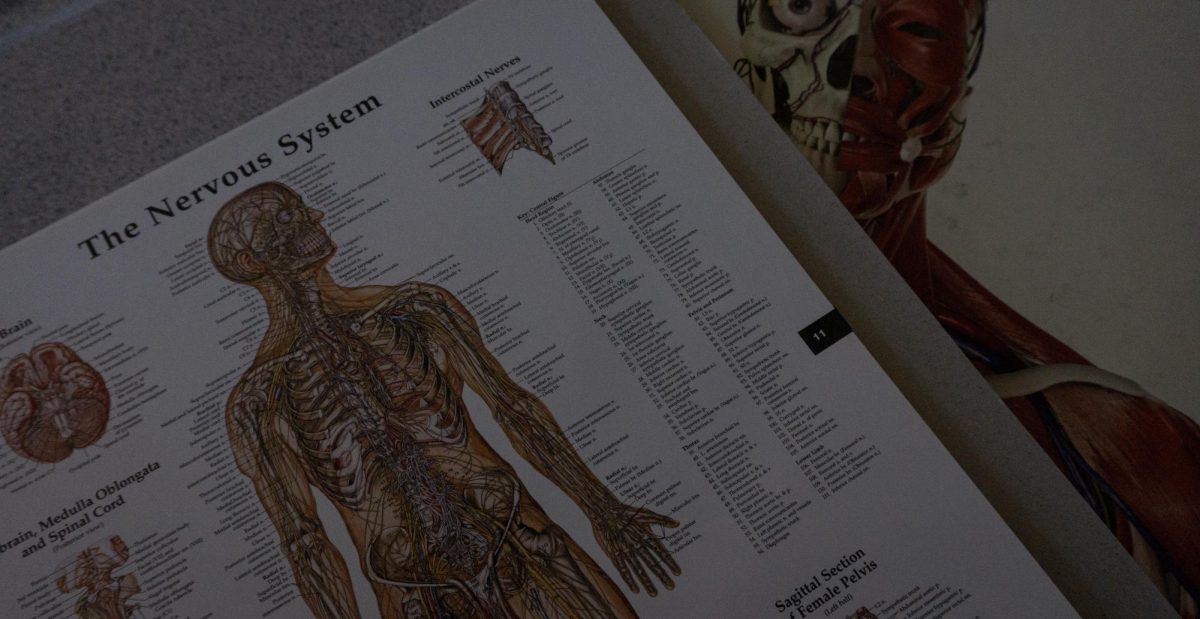
The steady metronome of a beating heart ticks faster as heavy rap music blasts through speakers. Unbeknownst to the heart, the body’s sympathetic nervous system is kicking into gear. This system of electrical impulses is responsible for activating the fight or flight response, which in turn results in increased heart rate. The antagonist to the sympathetic nervous system is the parasympathetic nervous system. When the parasympathetic system is stimulated, the body goes into a state of rest and digestion. This state releases the heart from its heavy pounding and allows the lungs to relax. If something as simple as the music we listen to can bring on these two drastically different states of being, what does that mean for our bodies each time we press the play button?
Fast paced music such as rap, hip hop, and pop have all been known to activate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Denmark’s AP Biology teacher Mr. Jeffrey explains that the “quick, sharp, and repetitious beats can activate the amygdala, hypothalamus and prefrontal cortex. These important locales within the brain process the music.” These musical notes cause the activation of the fight or flight response. When fight or flight is triggered, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone used to increase blood sugar. Adrenaline is also released. Adrenaline causes increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and the redirection of blood flow to the brain and muscles. The skin may appear flushed because blood is being rerouted. The body may also experience trembling, and the pupils will dilate to increase vision. Along with several types of music, stress, danger, and physical activity provoke the SNS.
“Whatever music we choose to listen to is driven by our innate drive for self-pleasure, therefore our music choices can influence creative thought, deeper analysis of any given topic, or simply make us happy.”
In addition to physical responses to rap, there are also emotional reactions that vary from person to person.The lyrics pertaining to many topics such as social issues, justice, violence, and more “can elicit the emotions of happiness, anger, rage, and depression,” Mr. Jeffrey shares. An individual’s connotations of the words sung along with their personal experiences with the concepts discussed can influence these responses. McKayla Team comments that rap music makes her “feel more motivated to work on either homework or soccer.” For her, the music hypes her up, but for someone else, rap may force them to relive angry or depressing memories.
On the other hand, classical and jazz music stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). Mr. Jeffrey notes that “The dulcet tones of classical music have been shown to reduce cortisol, blood pressure, and heart rate due to the release of dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins.” In this calmer condition, the body feels relaxed and often tired. This is a period of rest, and digestion occurs as well. The pupils will constrict to limit the light that enters the eyes, and changes are made to improve close up vision. Glands in the nose and mouth increase saliva and mucus production to aid digestion and breathing during rest. The heart rate is lowered, and muscles in the airways tighten to reduce the amount of work required by the lungs. Besides music, activities that encourage the body to rest and relax such as yoga and breathing exercises can help stimulate the PSNS.
Classical music often induces different emotions than rap music. Many people feel calmer, tired, or focused opposed to the stronger, more vibrant emotions felt during rap. Team agrees that she “[feels] more tired” when she listens to jazz or classical music.
While the great extent of science behind the music we listen to and how it affects our bodies is undeniable, it’s important to note that science cannot quantitatively measure how each individual responds to music on an emotional level. As Mr. Jeffrey points out, “we always have to consider the variables pertaining to the listener.” Each melomaniac brings unique life experiences to a song, and while their bodies will generally follow the trends found through science, responses are bound to vary. At the end of the day, Mr. Jeffrey concludes “that whatever music we choose to listen to is driven by our innate drive for self-pleasure, therefore our music choices can influence creative thought, deeper analysis of any given topic, or simply make us happy.” Studying the science behind the music is an enthralling adventure, but perhaps music’s most marvelous aspect is its ability to pierce our hearts and make us feel alive.
“Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS): What It Is & Function.” Cleveland Clinic, 6 June 2022, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23266-parasympathetic-nervous-system-psns.
“Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): What It Is & Function.” Cleveland Clinic, 6 June 2022, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23262-sympathetic-nervous-system-sns-fight-or-flight.